Nodes
Detailed information about all of Ragdoll's custom nodes along with the most commonly used attributes. For full attribute reference, see the link at the bottom of each node type, such as rdRigid.
Each Ragdoll node starts with
rd, e.g.rdRigid
Scene
Container of all rigids, constraints and forces that interact.
The scene represents the knowledge each simulation has, including rigids and their properties, constraints, forces. The works. There can be more than one Ragdoll scene in your Maya scene, but much like Maya scenes they cannot interact. The order in which scenes are simulated is also undefined, so you cannot expect e.g. fingers in one solver to run after the body in another solver.
Parallelism
Ragdoll scenes support both scene-level parallelism and node-level parallelism.
Scene-level parallelism happens when there are more than one Ragdoll scene present, each scene is then run in parallel for improved performance. For that reason, prefer using as many scenes as possible, especially if they are unlikely to interact.
Node-level Parallelism happens internally, whereby a single simulation is distributed over multiple threads. The behavior can be tuned via the rdScene.threadCount attribute. Keep this at 0 when your scenes are small, i.e. < 100 rigids. The overhead of splitting up a simulation outweighs the benefit unless there is a lot to split. You should notice a performance difference in either direction as you manipulate this attribute.
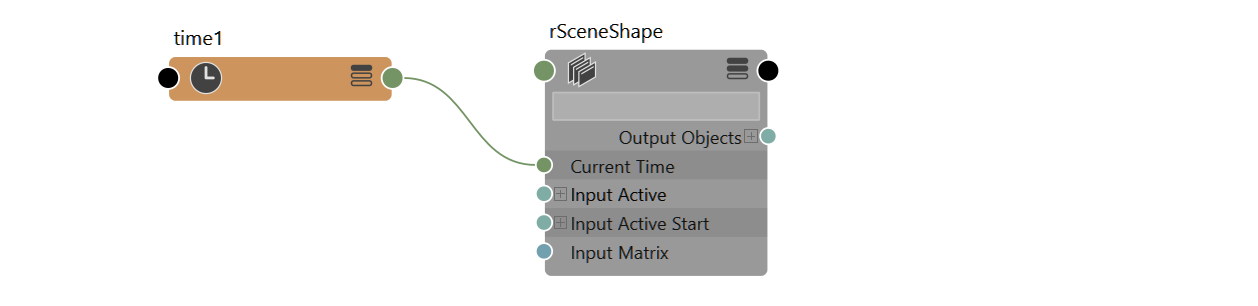
{{ node.rdScene.keyableAttributes }}
Rigid
A single transform in or out of Ragdoll.
The rigid is the physical equivalent of native Maya geometry. It can either feed into the simulation (passive) or come out of the simulation (active).
Active Rigidpass data from Ragdoll to MayaPassive Rigidpass data from Maya to Ragdoll
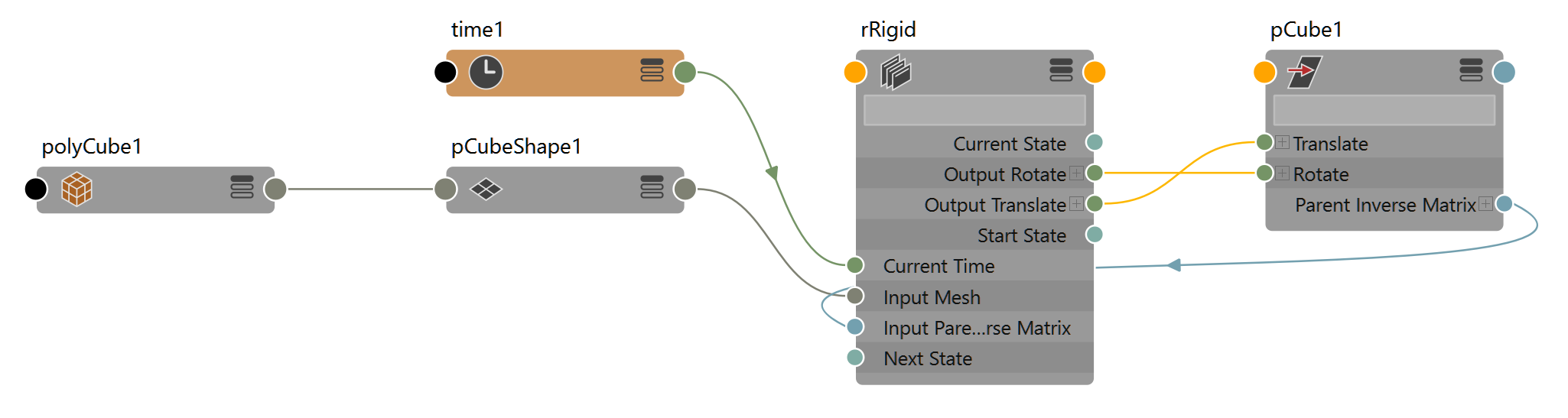
{{ node.rdRigid.keyableAttributes }}
Constraint
A relationship between two rigids.
Typically this relationship is something to limit one or more axes - e.g. translateXYZ and rotateZ - of one rigid relative another rigid, like a door "constrained" to a wall. In that case, the wall would be considered a "parent" and the door a "child".
However it is important to keep in mind that in the real world, there is no such thing. The door is as constrained to the wall as the wall is constrained to the door. This is especially apparent when the two constrained rigids are both active and have a similar mass, such as your upper and lower leg. As you bend your knee, both the thigh and lower leg are affected equally.
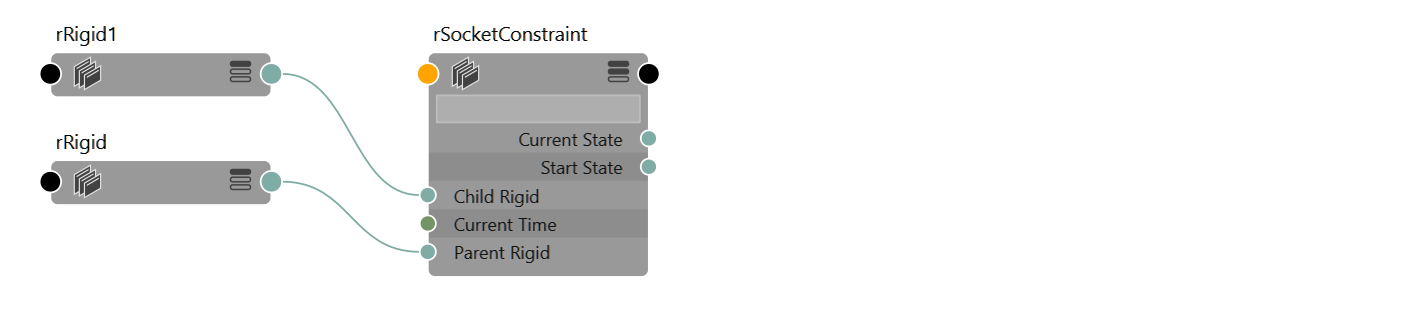
{{ node.rdConstraint.keyableAttributes }}
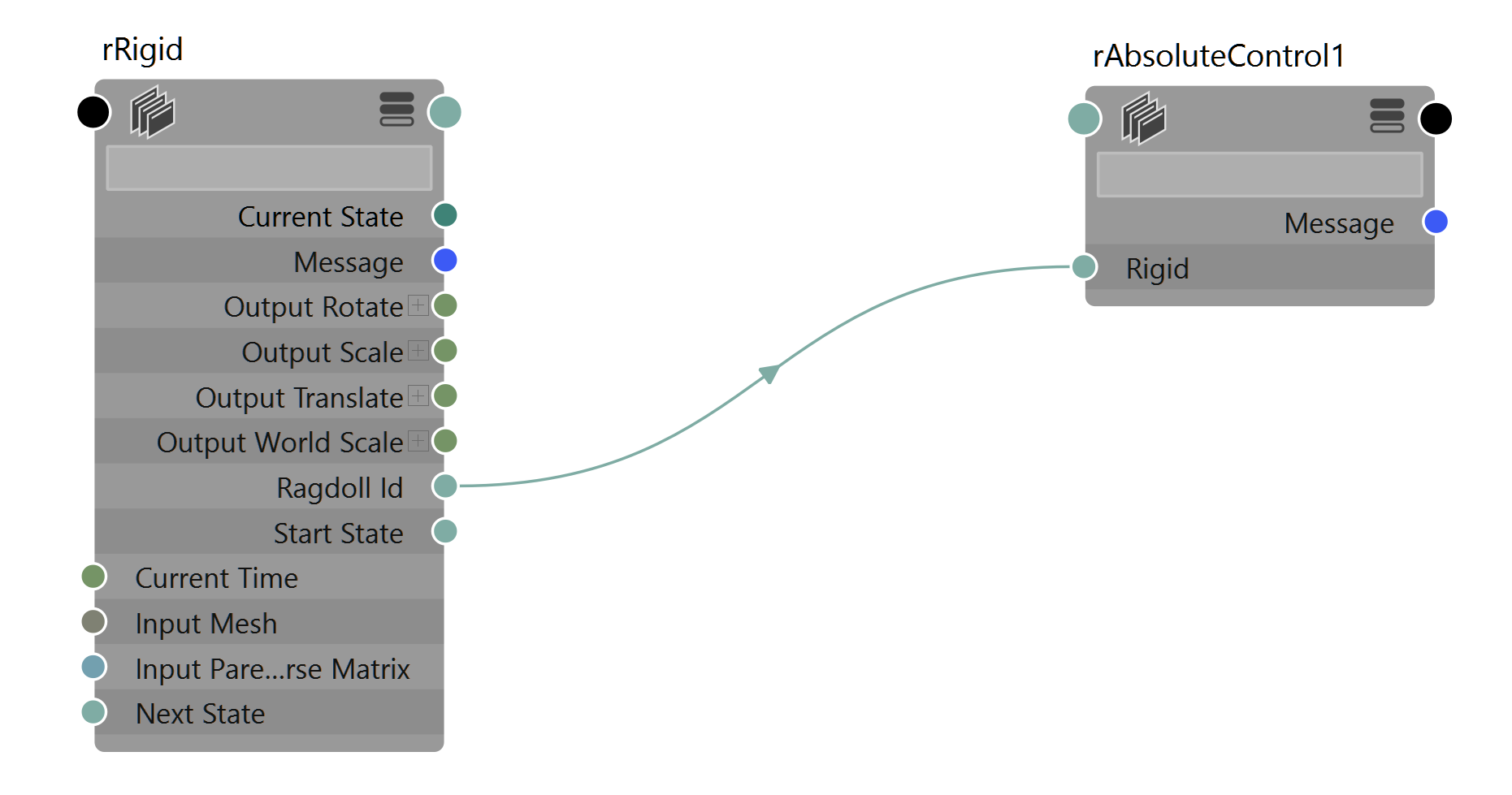
Control
A placeholder for drawing a rigid under a different transform.
This node is cosmetic only. It helps you spot the rigid and rigid orientation in the viewport for a standalone controller, like a Guide. It also draws the node with a special icon in the outliner. But that's about it!
Constraint Multiplier
Multiply one or more attributes of one or more constraints.
This node enables you to animate one attribute that affect many attributes, like Translate Guide Stiffness across an entire character or limb.
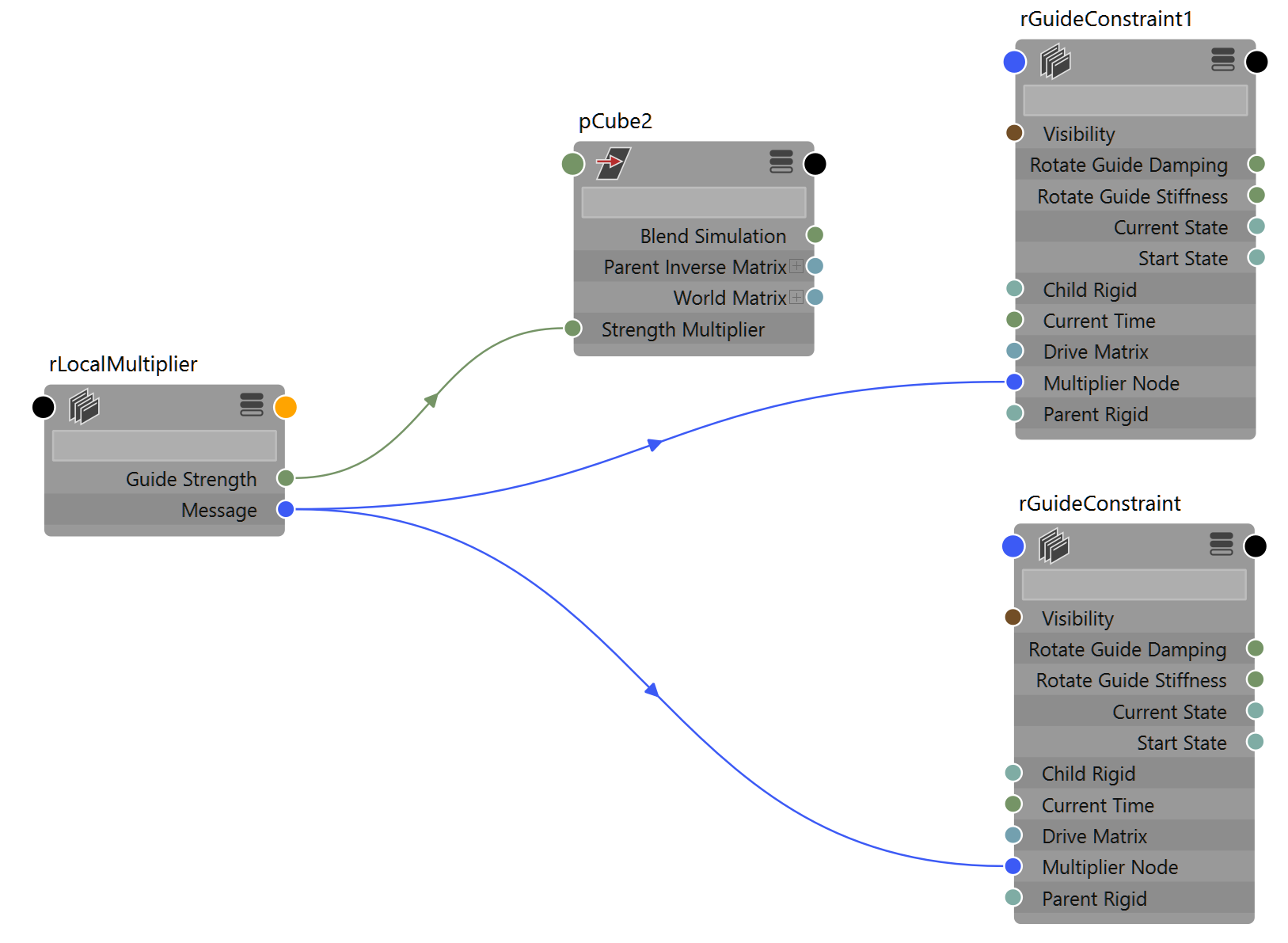
{{ node.rdConstraintMultiplier.keyableAttributes }}
Rigid Multiplier
Multiply one or more attributes of one or more rigids.
This node enables you to animate one attribute that affect many attributes, like Air Density across an entire character or limb.
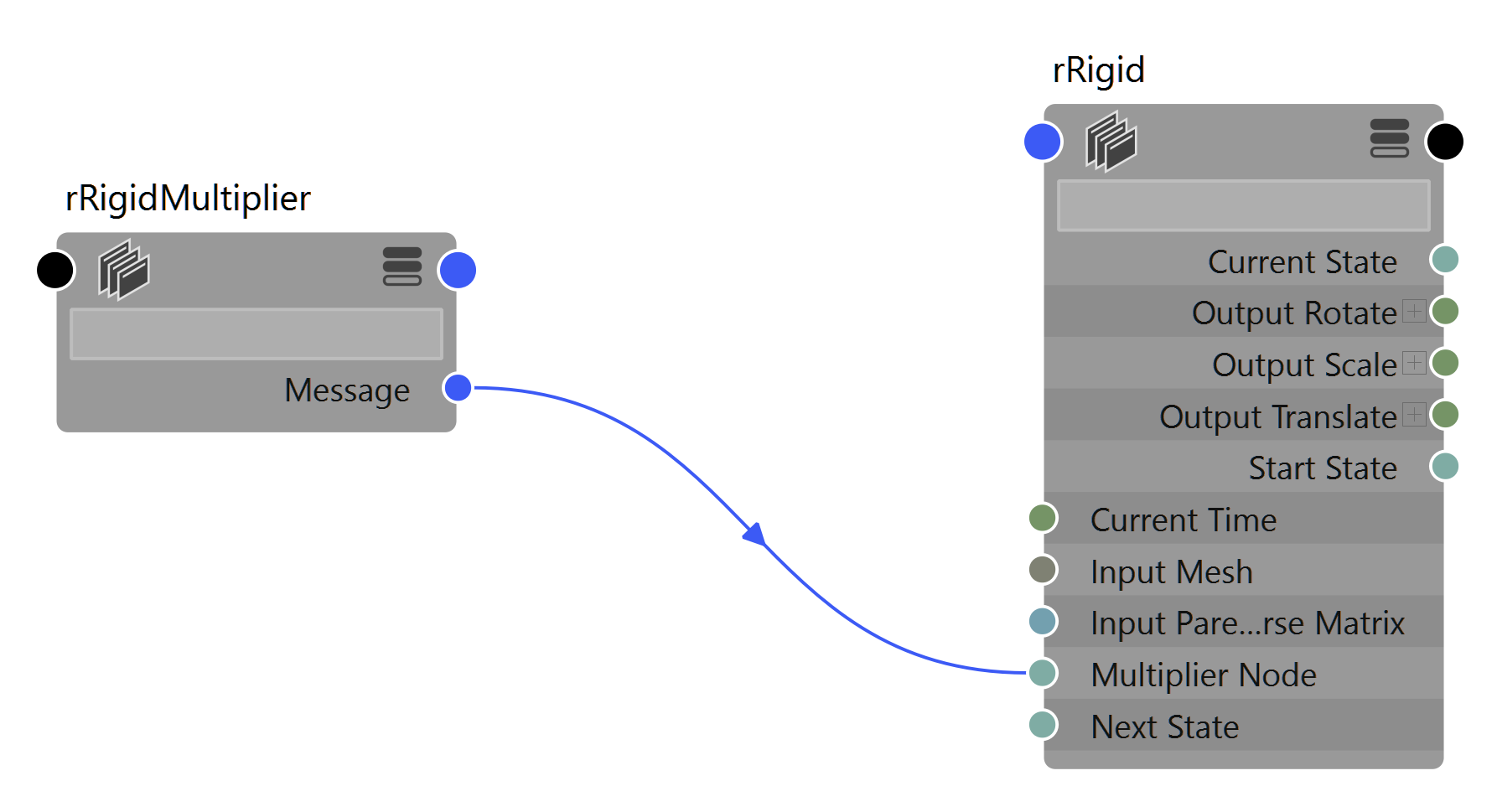
{{ node.rdRigidMultiplier.keyableAttributes }}
Other
Notes on general concepts used in Ragdoll.
Backwards Compatibility
- Default values never change, those written into the node type itself
- Initial values may change, those set during node-creation
This means previously authored scenes will always behave the same, whilst still enabling new default values for future versions and future authored physics.
Exclusive Nodes
Ragdoll consists of a few new native types, like rdRigid and rdConstraint. During creation, Ragdoll may generate Maya-native types too, like multMatrix and composeMatrix. Those nodes are exclusive to Ragdoll and should be removed alongside them. This is managed via the so-called .exclusiveNodes attribute on each Ragdoll node type.
User Attributes
Whenever Ragdoll attributes appear on your original animation controls, they are referred to as "user attributes" by Ragdoll and tracked via the .userAttributes attribute on each Ragdoll node. These attributes are exclusive to Ragdoll and are removed alongside the Ragdoll node types they interact with.